Opamp Current to Voltage Converter || Transimpedance Amplifier
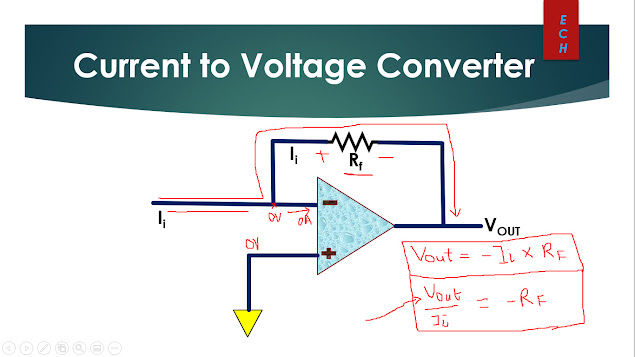
Opamp Current to Voltage Converter In this blog, I will explain Opamp Current to Voltage Converter, Why do we need current to voltage converter and application of Current to Voltage Converter. The complete explanation can be watched in video link given below. Understanding Transimpedance Amplifier : - Since no current enters the inverting input terminal and all of the current flows through the feedback resistance Rf on its way to output node. - The noninverting input terminal is connected to ground and we can assume inverting input is connected to ground due to virtual ground. -Since one side of feedback resistance Rf is connected to ground and other side is connected at Vout. So by ohms law the magnitude of output voltage is equal to the input current times feedback resistance. -The input to output relationship of transimpedance amplifier is given by: Vout = -Ii X Rf Vout/Ii = -Rf where Vout/Ii equal to transimpedance Transimpedance Amplifier vs Resistor : Why do we need Transimpeda